Why CORS Errors Happen in Web Apps
Why do CORS errors occur in web applications?
CORS errors occur when a web application attempts to access a resource from a different origin without the necessary permissions. This happens because the browser enforces a security policy called the Same Origin Policy, which restricts how a document or script loaded from one origin can interact with resources from another origin. If the external service does not return the 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header, the browser will block the request, resulting in a CORS error.
More related questions
What is a CORS error and how can I identify it?
A CORS error occurs when a web application tries to make a cross-origin request without the proper permissions. You can identify a CORS error by checking the browser's console for messages like 'No Access-Control-Allow-Origin header' or…
How can I troubleshoot CORS errors in my application?
To troubleshoot CORS errors, start by identifying the origin of the request and the external service being called. Check if the resource requires authentication and if an OPTIONS HTTP method call is made. If a redirect occurs before the OPTIONS…
What are some possible solutions for CORS errors?
Possible solutions for CORS errors include modifying the external server to return the 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header, using a back-end proxy server, or embedding the resource directly into the web app. However, these solutions may not always…
Can browser versions affect CORS error messages?
Yes, different browser versions can affect the CORS error messages you see. Although the CORS specification is a standard, browsers like Chrome and Firefox may return different console messages for the same error. It's important to be aware of…
What should I do if there's no fix for a CORS error?
If there's no fix for a CORS error, it might be because the resource is not meant to be shared in the context of a browser web app. The decision to share a resource lies with the resource owner, not the web app. In such cases, consider whether the…
Interested indeflectingover 70% of your Zendesk support tickets?

Zendesk Support Tickets
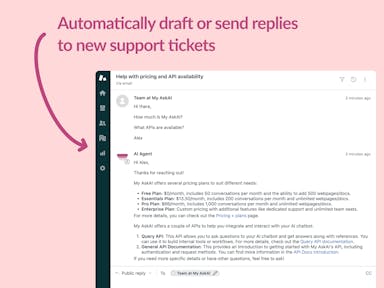

Zendesk Messaging (live chat)
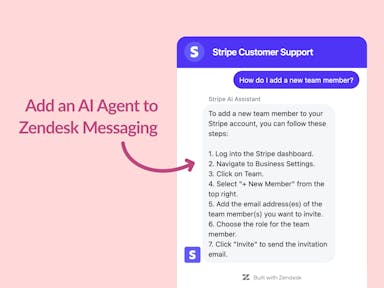
Join1,000+ companies reducing their support costs and freeing up support agents for more important work
“We needed an AI agent integrated within our current tools. My AskAI was the only solution that wasn't going to disrupt our operations.”
Zeffy
“At the end of last year I was given the challenge - how can we provide the same or better service, without hiring anyone?”
Zinc
“My AskAI blew everybody else out of the water. It made the selection process very easy for us.”
Customer.io($50M+ ARR)

“It now resolves 71% of queries (over 35,000 every month), meaning more time solving complex issues and improving UX.”
Freecash

“We needed an AI agent integrated within our current tools. My AskAI was the only solution that wasn't going to disrupt our operations.”
Zeffy

“At the end of last year I was given the challenge - how can we provide the same or better service, without hiring anyone?”
Zinc

“My AskAI blew everybody else out of the water. It made the selection process very easy for us.”
Customer.io($50M+ ARR)
“It now resolves 71% of queries (over 35,000 every month), meaning more time solving complex issues and improving UX.”
Freecash







Reduce support costs.Spend more time on customer success.

