Practical Examples of Using Median in Reports
What are some practical examples of using median in reports?
Using the median in reports is beneficial when dealing with skewed data or outliers. For instance, when reporting on full resolution time, using the median can provide a clearer picture because some tickets may have been under investigation for a long time, skewing the average.
Similarly, for metrics like first reply time, where the data is generally consistent, the median can help filter out anomalies, such as proactive tickets created by agents that might have a high first reply time. These examples show how the median can offer a more accurate representation of central tendency in certain scenarios.
More related questions
What is the difference between average and median in data analysis?
The average and median are both measures of central tendency, but they differ in how they handle data. The average, or mean, is calculated by adding all the values in a dataset and dividing by the number of values. It is best used for datasets with…
When should I use median instead of average?
You should use the median instead of the average when your dataset contains outliers or is skewed. The median is a better measure of central tendency in these cases because it is not influenced by extreme values, unlike the average. For instance,…
How do you calculate the average and median?
Calculating the average and median involves different methods. To find the average, add up all the values in your dataset and divide the sum by the total number of values. This gives you the arithmetic mean, which is useful for normally distributed…
Why might the average and median differ significantly?
The average and median can differ significantly in datasets with outliers or skewed distributions. The average is sensitive to extreme values, which can inflate or deflate the mean, making it less representative of the central tendency. For…
Interested indeflectingover 70% of your Zendesk support tickets?

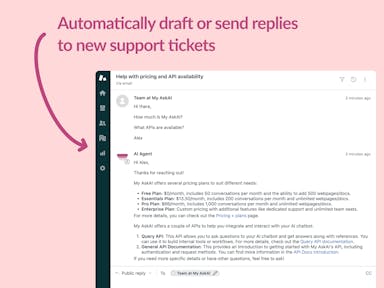
Zendesk Support Tickets

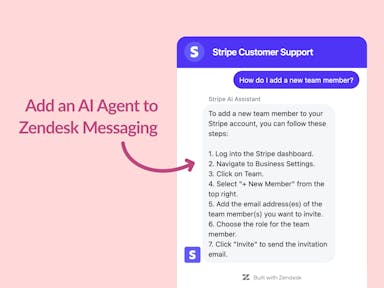
Zendesk Messaging (live chat)
Join1,000+ companies reducing their support costs and freeing up support agents for more important work
“We needed an AI agent integrated within our current tools. My AskAI was the only solution that wasn't going to disrupt our operations.”
Zeffy
“At the end of last year I was given the challenge - how can we provide the same or better service, without hiring anyone?”
Zinc
“My AskAI blew everybody else out of the water. It made the selection process very easy for us.”
Customer.io($50M+ ARR)

“It now resolves 71% of queries (over 35,000 every month), meaning more time solving complex issues and improving UX.”
Freecash

“We needed an AI agent integrated within our current tools. My AskAI was the only solution that wasn't going to disrupt our operations.”
Zeffy

“At the end of last year I was given the challenge - how can we provide the same or better service, without hiring anyone?”
Zinc

“My AskAI blew everybody else out of the water. It made the selection process very easy for us.”
Customer.io($50M+ ARR)
“It now resolves 71% of queries (over 35,000 every month), meaning more time solving complex issues and improving UX.”
Freecash







Reduce support costs.Spend more time on customer success.

